Portal:Rocketry
The Rocketry Portal

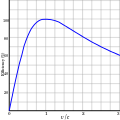
A rocket (from Italian: rocchetto, lit. 'bobbin/spool') is a vehicle that uses jet propulsion to accelerate without using the surrounding air. A rocket engine produces thrust by reaction to exhaust expelled at high speed. Rocket engines work entirely from propellant carried within the vehicle; therefore a rocket can fly in the vacuum of space. Rockets work more efficiently in a vacuum and incur a loss of thrust due to the opposing pressure of the atmosphere.
Multistage rockets are capable of attaining escape velocity from Earth and therefore can achieve unlimited maximum altitude. Compared with airbreathing engines, rockets are lightweight and powerful and capable of generating large accelerations. To control their flight, rockets rely on momentum, airfoils, auxiliary reaction engines, gimballed thrust, momentum wheels, deflection of the exhaust stream, propellant flow, spin, or gravity.
Rockets for military and recreational uses date back to at least 13th-century China. Significant scientific, interplanetary and industrial use did not occur until the 20th century, when rocketry was the enabling technology for the Space Age, including setting foot on the Moon. Rockets are now used for fireworks, missiles and other weaponry, ejection seats, launch vehicles for artificial satellites, human spaceflight, and space exploration.
Chemical rockets are the most common type of high power rocket, typically creating a high speed exhaust by the combustion of fuel with an oxidizer. The stored propellant can be a simple pressurized gas or a single liquid fuel that disassociates in the presence of a catalyst (monopropellant), two liquids that spontaneously react on contact (hypergolic propellants), two liquids that must be ignited to react (like kerosene (RP1) and liquid oxygen, used in most liquid-propellant rockets), a solid combination of fuel with oxidizer (solid fuel), or solid fuel with liquid or gaseous oxidizer (hybrid propellant system). Chemical rockets store a large amount of energy in an easily released form, and can be very dangerous. However, careful design, testing, construction and use minimizes risks. (Full article...)
Selected article -

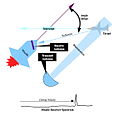
Rocket Lab USA, Inc. is a publicly traded aerospace manufacturer and launch service provider that operates and launches lightweight Electron orbital rockets used to provide dedicated launch services for small satellites as well as a suborbital variant of Electron called HASTE (Hypersonic Accelerator Suborbital Test Electron). The company plans to build a larger Neutron rocket as early as 2025. Electron rockets have launched to orbit 47 times from either Rocket Lab's Launch Complex 1 in New Zealand or at the Mid-Atlantic Regional Spaceport in Wallops Island, Virginia, United States. Rocket Lab has launched one sub-orbital HASTE rocket to date from Wallops Island, Virginia. In addition to the Electron, Neutron, and HASTE launch vehicles, Rocket Lab manufactures and operates spacecraft and is a supplier of satellite components including star trackers, reaction wheels, solar cells and arrays, satellite radios, separation systems, as well as flight and ground software.
The company was founded in New Zealand in 2006. By 2009, the successful launch of Ātea-1 made the organization the first private company in the Southern Hemisphere to reach space. The company established headquarters in California, US in 2013 and developed the expendable Electron rocket. The first launch of the rocket took place in May 2017. In August 2021, the company became a public company, listed on the Nasdaq stock exchange through a SPAC merger. In May 2022, after four years of development, the Electron booster attempted recovery by a helicopter.In 2024, the company announced that a first stage booster that was recovered on an earlier launch will be reused on a future launch, marking the first time Electron would reuse the full first stage.In August 2020 the company launched its first in-house designed and built satellite, Photon. (Full article...)In the news
- 26 May 2024 – Israel–Hamas war
- The Al-Qassam Brigades fire rockets towards Tel Aviv, Israel, for the first time in four months. (BBC News) (El Confidencial)
- 22 May 2024 –
- Russia launches a Soyuz-2 rocket carrying the Kosmos 2576 satellite from the Plesetsk Cosmodrome launch site in Arkhangelsk Oblast. The United States Space Command accuses it of being an anti-satellite weapon capable of attacking other satellites, and is in the same orbit as a satellite operated by the National Reconnaissance Office. (Al Jazeera)
- 19 May 2024 – Russian invasion of Ukraine
- At least six people are killed and 27 others are injured in a Russian double tap missile strike on a recreation area near Kharkiv. Separately, five people are killed and nine others are injured in a Russian strike using a multiple launch rocket system on two villages in Kupiansk Raion, Kharkiv Oblast. (Reuters)
- 10 May 2024 – M23 offensive
- The death toll from rocket strikes on an IDP camp in Goma, Democratic Republic of the Congo, increases to 35. (AP)
- 7 May 2024 – M23 offensive
- The death toll from rocket strikes on an IDP camp in Goma, Democratic Republic of the Congo, increases to 18. (Reuters)
- 5 May 2024 – Israel–Hamas war
- Israeli air raids in Meiss Ej Jabal, Lebanon, cause "massive destruction" according to a Lebanese state-run agency, killing four civilians and injuring three others. In response, Hezbollah fires dozens of Katyusha and Falaq rockets towards Kiryat Shmona, Israel. (Reuters)
Topics
List articles
Things to do
 |
Here are some tasks awaiting attention:
|
Wikimedia
The following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
-
Commons
Free media repository -
Wikibooks
Free textbooks and manuals -
Wikidata
Free knowledge base -
Wikinews
Free-content news -
Wikiquote
Collection of quotations -
Wikisource
Free-content library -
Wikispecies
Directory of species -
Wikiversity
Free learning tools -
Wikivoyage
Free travel guide -
Wiktionary
Dictionary and thesaurus