Portal:Asia

 Asia (/ˈeɪʒə/ AY-zhə, UK also /ˈeɪʃə/ AY-shə) is the largest continent in the world by both land area and population. It covers an area of more than 44 million square kilometers, about 30% of Earth's total land area and 8% of Earth's total surface area. The continent, which has long been home to the majority of the human population, was the site of many of the first civilizations. Its 4.7 billion people constitute roughly 60% of the world's population. Asia shares the landmass of Eurasia with Europe, and of Afro-Eurasia with both Europe and Africa. In general terms, it is bounded on the east by the Pacific Ocean, on the south by the Indian Ocean, and on the north by the Arctic Ocean. The border of Asia with Europe is a historical and cultural construct, as there is no clear physical and geographical separation between them. It is somewhat arbitrary and has moved since its first conception in classical antiquity. The division of Eurasia into two continents reflects East–West cultural, linguistic, and ethnic differences, some of which vary on a spectrum rather than with a sharp dividing line. A commonly accepted division places Asia to the east of the Suez Canal separating it from Africa; and to the east of the Turkish Straits, the Ural Mountains and Ural River, and to the south of the Caucasus Mountains and the Caspian and Black seas, separating it from Europe. China and India traded places as the largest economies in the world from 1 to 1800 CE. China was a major economic power for much of recorded history, with the highest GDP per capita until 1500. The Silk Road became the main east–west trading route in the Asian hinterlands while the Straits of Malacca stood as a major sea route. Asia has exhibited economic dynamism as well as robust population growth during the 20th century, but overall population growth has since fallen. Asia was the birthplace of most of the world's mainstream religions including Hinduism, Zoroastrianism, Judaism, Jainism, Buddhism, Confucianism, Taoism, Christianity, Islam, Sikhism, as well as many other religions. (Full article...) Featured articleThe Tang dynasty (/tɑːŋ/, [tʰǎŋ]; Chinese: 唐朝), or the Tang Empire, was an imperial dynasty of China that ruled from 618 to 907, with an interregnum between 690 and 705. It was preceded by the Sui dynasty and followed by the Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms period. Historians generally regard the Tang as a high point in Chinese civilization, and a golden age of cosmopolitan culture. Tang territory, acquired through the military campaigns of its early rulers, rivaled that of the Han dynasty. The Li family founded the dynasty after taking advantage of a period of Sui decline and precipitating their final collapse, in turn inaugurating a period of progress and stability in the first half of the dynasty's rule. The dynasty was formally interrupted during 690–705 when Empress Wu Zetian seized the throne, proclaiming the Wu Zhou dynasty and becoming the only legitimate Chinese empress regnant. The devastating An Lushan Rebellion (755–763) shook the nation and led to the decline of central authority in the dynasty's latter half. Like the previous Sui dynasty, the Tang maintained a civil-service system by recruiting scholar-officials through standardized examinations and recommendations to office. The rise of regional military governors known as jiedushi during the 9th century undermined this civil order. The dynasty and central government went into decline by the latter half of the 9th century; agrarian rebellions resulted in mass population loss and displacement, widespread poverty, and further government dysfunction that ultimately ended the dynasty in 907. (Full article...)Selected Country Singapore, officially the Republic of Singapore, is an island country and city-state in maritime Southeast Asia. It is located about one degree of latitude (137 kilometres or 85 miles) north of the equator, off the southern tip of the Malay Peninsula, bordering the Strait of Malacca to the west, the Singapore Strait to the south along with the Riau Islands in Indonesia, the South China Sea to the east, and the Straits of Johor along with the State of Johor in Malaysia to the north. The country's territory comprises one main island, 63 satellite islands and islets, and one outlying islet; the combined area of these has increased by approximately 25% since the country's independence as a result of extensive land reclamation projects. It has the second highest population density of any country in the world, although there are numerous green and recreational spaces as a result of urban planning. With a multicultural population and in recognition of the cultural identities of the major ethnic groups within the nation, Singapore has four official languages: English, Malay, Mandarin, and Tamil. English is the common language, with its exclusive use in numerous public services. Multi-racialism is enshrined in the constitution and continues to shape national policies in education, housing, and politics. Singapore's history dates back at least eight hundred years, having been a maritime emporium known as Temasek and subsequently a major constituent part of several successive thalassocratic empires. Its contemporary era began in 1819, when Stamford Raffles established Singapore as an entrepôt trading post of the British Empire. In 1867, the colonies in Southeast Asia were reorganised, and Singapore came under the direct control of Britain as part of the Straits Settlements. During World War II, Singapore was occupied by Japan in 1942 and returned to British control as a separate Crown colony following Japan's surrender in 1945. Singapore gained self-governance in 1959 and, in 1963, became part of the new federation of Malaysia, alongside Malaya, North Borneo, and Sarawak. Ideological differences, most notably the perceived encroachment of the egalitarian "Malaysian Malaysia" political ideology led by Lee Kuan Yew into the other constituent entities of Malaysia—at the perceived expense of the bumiputera and the policies of Ketuanan Melayu—eventually led to Singapore's expulsion from the federation two years later; Singapore became an independent sovereign country in 1965. (Full article...)Featured biographyAlbertus Soegijapranata, SJ (Indonesian: [alˈbərtʊs suˈɡijapraˈnata]; Perfected Spelling: Albertus Sugiyapranata; 25 November 1896 – 22 July 1963), better known by his birth name Soegija, was a Jesuit priest who became the Apostolic Vicar of Semarang and later its archbishop. He was the first native Indonesian bishop and known for his pro-nationalistic stance, often expressed as "100% Catholic 100% Indonesian". Soegija was born in Surakarta, Dutch East Indies, to a Muslim courtier and his wife. The family moved to nearby Yogyakarta when Soegija was still young; there he began his education. Known as a bright child, around 1909 he was asked by Father Frans van Lith to enter Xaverius College, a Jesuit school in Muntilan, where Soegija slowly became interested in Catholicism. He was baptised on 24 December 1910. After graduating from Xaverius in 1915 and spending a year as a teacher there, Soegija spent two years at the on-site seminary before going to the Netherlands in 1919. He began his two-year novitiate with the Society of Jesus in September 1920 in Grave, and finished his juniorate there in 1923. After three years studying philosophy at Berchmann College in Oudenbosch, he was sent back to Muntilan as a teacher for a further two years. In 1928, he returned to the Netherlands to study theology at Maastricht, where he was ordained by Bishop of Roermond Laurentius Schrijnen on 15 August 1931; Soegija then added the word "pranata" to the back of his name. He was then sent back to the Indies to preach and became a parochial vicar at the parish in Kidul Loji, Yogyakarta, and in 1934 he was given his own parish in Bintaran. There he focused on creating a sense of Catholicism within the native community, emphasising the need for strong bonds between Catholic families. Soegijapranata was consecrated as the vicar apostolic of the newly established Apostolic Vicariate of Semarang in 1940. (Full article...)General imagesThe following are images from various Asia-related articles on Wikipedia. Featured picture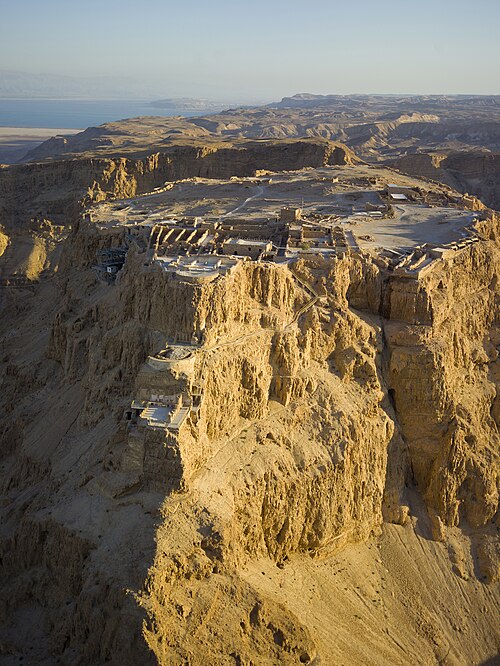 Credit: Photograph: Andrew Shiva An aerial view of Masada, an ancient fortification in the Southern District of Israel. Found atop an isolated rock plateau, it overlooks the Dead Sea. The first fortifications on the mountain were built by Alexander Jannaeus, and significantly strengthened by the Roman client king Herod between 37 and 31 BCE. During the First Jewish–Roman War of 66–73 CE, the fortress was besieged, falling only after the 960 Sicarii defending it committed mass suicide.
Masada is among the more popular tourist attractions in Israel, and in 2001 it was made a UNESCO World Heritage Site.
Did you know...
Updated: 6:33, 14 February 2024 In the news
Related portalsMajor Religions in Asia Middle East Central Asia and Surroundings Indian Subcontinent Southeast Asia East Asia Selected panorama
A panoramic view of the Hiroshima Peace Memorial, the site of the first atomic bomb to be used in warfare on August 6, 1945, during the final stages of World War II. Over 70,000 people were killed immediately, and another 70,000 suffered fatal injuries from the radiation, after the U.S. Army Air Force bomber Enola Gay dropped the bomb, codenamed "Little Boy". The Genbaku ("A-bomb") Dome (center) was directly beneath the blast, but managed to survive mostly intact. TopicsCategoriesAssociated WikimediaThe following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
More portalsShortcuts to this page: Asia portal • P:ASIA Purge server cache |